Hash functions are used to securely store passwords, find duplicate records, quickly store and retrieve data, among other useful computational tasks. As a practical example, all user passwords on boot.dev are hashed using Bcrypt to ensure that if an attacker were ever to gain access to our database our user’s passwords wouldn’t be compromised.
I want to focus on several important features of cryptographic hash functions, arguably the most important features:
- Hash functions scramble data deterministically
- No matter the input, the output of a hash function always has the same size
- The original data can not be retrieved from the scrambled data (one-way function)
Other hash function explainers 🔗
If you’re looking for an explanation of a different hash function, we may have you covered
Hash Functions Scramble Data Deterministically 🔗
Think of a Rubix cube.

I start with the cube unscrambled. If I start twisting randomly, by the end I will end up with something that does not resemble anything close to what I started with. Also, if I were to start over and do the exact same series of moves, I would be able to repeatedly get the exact same outcome. Even though the outcome may appear random, it isn’t at all. That is what deterministic means.
Determinism is important for securely storing a password. For instance, let’s pretend my password is “iLoveBitcoin”
I can use a hash function to scramble it:
iLoveBitcoin → “2f5sfsdfs5s1fsfsdf98ss4f84sfs6d5fs2d1fdf15”
Now, if anyone were to see the scrambled version, they wouldn’t know my original password! This is important because it means that as a website developer, I only need to store the hash (scrambled data) of my user’s password to be able to verify them. When the user signs up, I hash the password and store it in my database. When the user logs in, I just hash what they typed in and compare the two hashes. Because a given input always produces the same hash, this works every time.
If a website stores passwords in plain-text (not hashed) it is a huge breach of security. If someone were to hack that site’s database and find all the emails stored with plain-text passwords, they could then use those combinations and try them on other websites.
No Matter the Input, the Output is the Same Size 🔗
If I hash a single word the output will be a certain size (in the case of SHA-256, a particular hashing function, the size is 256 bits). If I hash a book, the output will be the same size.
This is another important feature because it can save us computing time. A classic example is using a hash as a key in a data map. A data map is a simple structure used in computer science to store data.
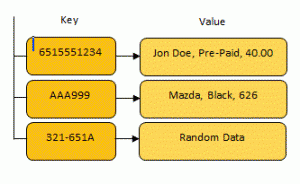
When a program stores data in a map, a key and value are given to the map. When a program wants to access the value, it can give the appropriate key to the map and receive the corresponding value. Data maps are good because they can find data instantly. The key is used as an address that the computer can find immediately, instead of taking hours searching through millions of records.
Because keys are like addresses, they can’t be too large. If I want to store books in a data map I can hash the contents of the book and use the hash as a key. As a programmer, I can simply use the hash to look up the contents of the book instead of trying to sort through thousands of records by title, author, etc.
How Do They Work? 🔗
Here is the real challenge of writing this article. I’m going to keep it extremely simple and omit the actual implementation details while giving you a basic idea of what the computer actually does when it hashes some data.
Let’s walk through an example algorithm I’m making up on the fly for this demonstration, LANEHASH:
- We start with some data to hash
iLoveBitcoin
- I convert the letters and numbers into 1’s and 0’s (All data in computers are stored in 1’s and 0’s, different patterns of 1’s and 0’s represent different letters)
iLoveBitcoin→ 100010100000101111
- At this point we go through various predetermined steps to transform our data. The steps can be anything, the important thing is that whenever we use LANEHASH we need to use the same steps so that our algorithm is deterministic.
- We move the first four bits from the left side to the right
100010100000101111 → 101000001011111000
- We separate every other bit
101000001011111000 → 110011110 & 000001100
- We convert those two parts into base 10 numbers. Base 10 is the “normal” number system that we all learned in school. (all binary data really just number, you can look up how it converts binary to base 10 easily online elsewhere)
110011110 → 414
000001100→ 12
- We multiply the two numbers together
414 *12 = 4968
- We square that number
4968 ^ 2 = 24681024
- We convert that number back to binary
24681024 →1011110001001101001000000
- We chop 9 bits off the right side to get exactly 16 bits
1011110001001101001000000 → 1011110001001101
- We convert that binary data back to English
1011110001001101 → “8sj209dsns02k2”
As you can see, if you start with the same word at the beginning, you will always get the same output at the end. However, if you even change one letter, the outcome will be drastically changed.
Disclaimer 🔗
On the steps where I convert from English to binary, and from binary to English, I followed no pattern. Don’t let that confuse you. There are many different ways to convert binary data to English and back, I just didn’t want to get hung up on that in this article.




