Singletons are fairly controversial as far as I can tell, especially in JavaScript programming. Let’s take a look at what they are, when to (maybe) use them, and when not to.
What is a Singleton? 🔗
A singleton is a class that allows only a single instance of itself to be created and gives access to that created instance. It contains static variables that can accommodate unique and private instances of itself. We use it in scenarios when a user wants to restrict instantiation of a class to only one object. This is helpful usually when a single object is required to coordinate actions across a system.
Usually, in object-oriented programming, the idea is to define classes and create multiple instances of that class, each with its own state. This keeps code DRY and easy to maintain.
By contrast, it only instantiates a singleton once, and therefore any code that accesses the singleton will either:
- Create a new instance
- Read, update, or modify that instance
Which means a singleton is almost a global instance of a class. Gross.
I Can’t Believe It’s Not Global! 🔗
For the purpose of this article, we will assume we are using ES6 modules in our front-end React or Vue project. An example of a singleton we might want could be:
// Define our state and initialize it
let darkMode = false;
// Define the functions that will expose that state
const Settings = {
setDarkMode: (newVal) => (darkMode = newVal),
getDarkMode: () => darkMode,
};
// Disallow new properties on our object
Object.freeze(Settings);
export default Settings;
As stated earlier, a singleton is dangerously close to being a global variable, and we don’t like those. There is one important difference:
The singleton instance isn’t truly scoped globally: to modify the state, the caller must import the class and use getters and setters. This makes access more explicit and controlled. Not only are the ways in which the state can be modified explicitly defined, but files that use the state must ‘import’ it.
But Muh Redux 🔗
Here’s my over-simplified opinion in the form of a flowchart:
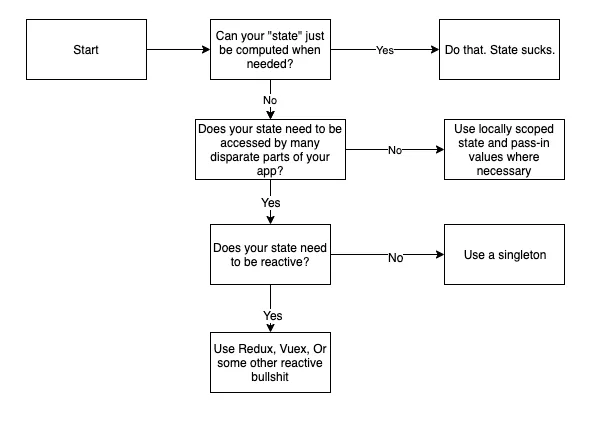
The idea is to use the simplest, most-controlled solution we reasonably can. In order of least evil –> most evil:
- scoped constants
- scoped variables
- singletons
- redux/vuex
- global variables
Singletons Suck 🔗
Redux, Vuex, singletons, and global variables all suck. Try not to use them. I’m just trying to point out that they all suck to varying degrees. Good luck.