In this tutorial, we’ll go step-by-step through building a video streaming API (which will work for music as well) in Go. Don’t worry, it’s surprisingly easy to build a robust media streaming server, especially if we utilize a modern communication protocol, HLS.
What is HLS? 🔗
HTTP Live Streaming is an HTTP-Based adaptive bitrate streaming communications protocol developed by Apple.
HLS is a streaming protocol that allows large media files to be served as many smaller text files that are broken up into roughly ~10-second increments. By breaking them up, the user’s client-side application only needs to buffer ~10 seconds in advance. This saves the user a lot of potential bandwidth and allows songs or videos to start playback almost immediately.
Using FFmpeg, we can easily convert mp3 files to HLS format, which consists of multiple files. One of these files contains the metadata (.m3u8) and is served first. This metadata file tells the client where to get each data file, and what each data file contains. The data files have a .ts extension and typically contain ~10 seconds of audio and are served one-at-a-time at the client’s request.

Get Started - Format Some Media for your Server 🔗
Download a sample .mp3:
http://www.hubharp.com/web_sound/BachGavotteShort.mp3
Install FFmpeg. If you are on a Mac:
brew install ffmpeg
Navigate to the directory of the mp3 file and run:
ffmpeg -i BachGavotteShort.mp3 -c:a libmp3lame -b:a 128k -map 0:0 -f segment -segment_time 10 -segment_list outputlist.m3u8 -segment_format mpegts output%03d.ts
This should result in three new files:
output000.ts output001.ts outputlist.m3u8
Congratulations! You are done with the hard part, you now have simple files that can be served over HTTP. Any modern client-side media library will know how to read HLS files.
Building the Streaming Server 🔗
As I eluded to above, HLS is very simple on the server-side. All we need to do is serve a path to the .m3u8 file, and make sure the .ts files are served from the same path. In traditional file server architecture, this just means that they need to be in the same directory.
Let’s set up our project with the following folder structure:
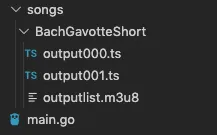
Copy the following code into main.go:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// configure the songs directory name and port
const songsDir = "songs"
const port = 8080
// add a handler for the song files
http.Handle("/", addHeaders(http.FileServer(http.Dir(songsDir))))
fmt.Printf("Starting server on %v\n", port)
log.Printf("Serving %s on HTTP port: %v\n", songsDir, port)
// serve and log errors
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(fmt.Sprintf(":%v", port), nil))
}
// addHeaders will act as middleware to give us CORS support
func addHeaders(h http.Handler) http.HandlerFunc {
return func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*")
h.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
}
Now run the server:
go run main.go
Your server is live! Test your code and listen to the music stream by using an HLS media client. You can find a free online client here
Simply paste your song’s URI and listen:
http://localhost:8080/bachgavotteshort/outputlist.m3u8